Containerization
Lesson Notes
Video
Introduction
History of running a software
- Early on, organizations ran applications on physical servers.
- Install or use an existing operating system.
- Install the tools needed by your software.
- Install dependencies of your software.
- Run your software.
Traditional Deployment
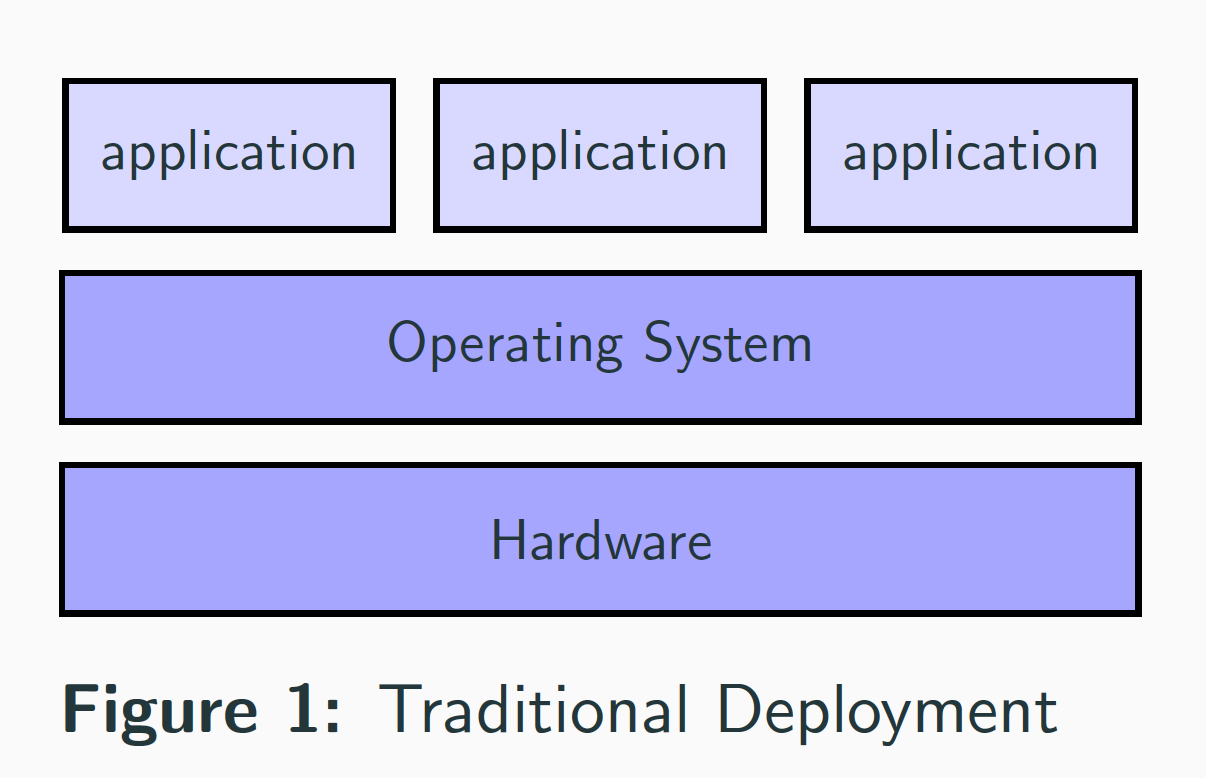
Issues with traditional deployment
- Isolation issue, no way to define resource boundaries for applications in a physical server, and this caused resource allocation issues.
- Scaling issues as resources were underutilized.
- It was expensive for organizations to maintain many physical servers.
Virtualization
Virtual Machines! How is virtualization possible?
- Virtualizing hardware produces virtual machines (VMs).
- Virtualization allows you to run multiple VMs on a single physical server. Each VM includes a full copy of an operating system, the application, necessary binaries, and libraries - taking up tens of GBs.
- Virtualization allows more effortless adding and updating of applications that solve the scalability issue.
- Virtualization allows better utilization of resources.
- Virtualization isolates applications between VMs.
Virtualization Deployment
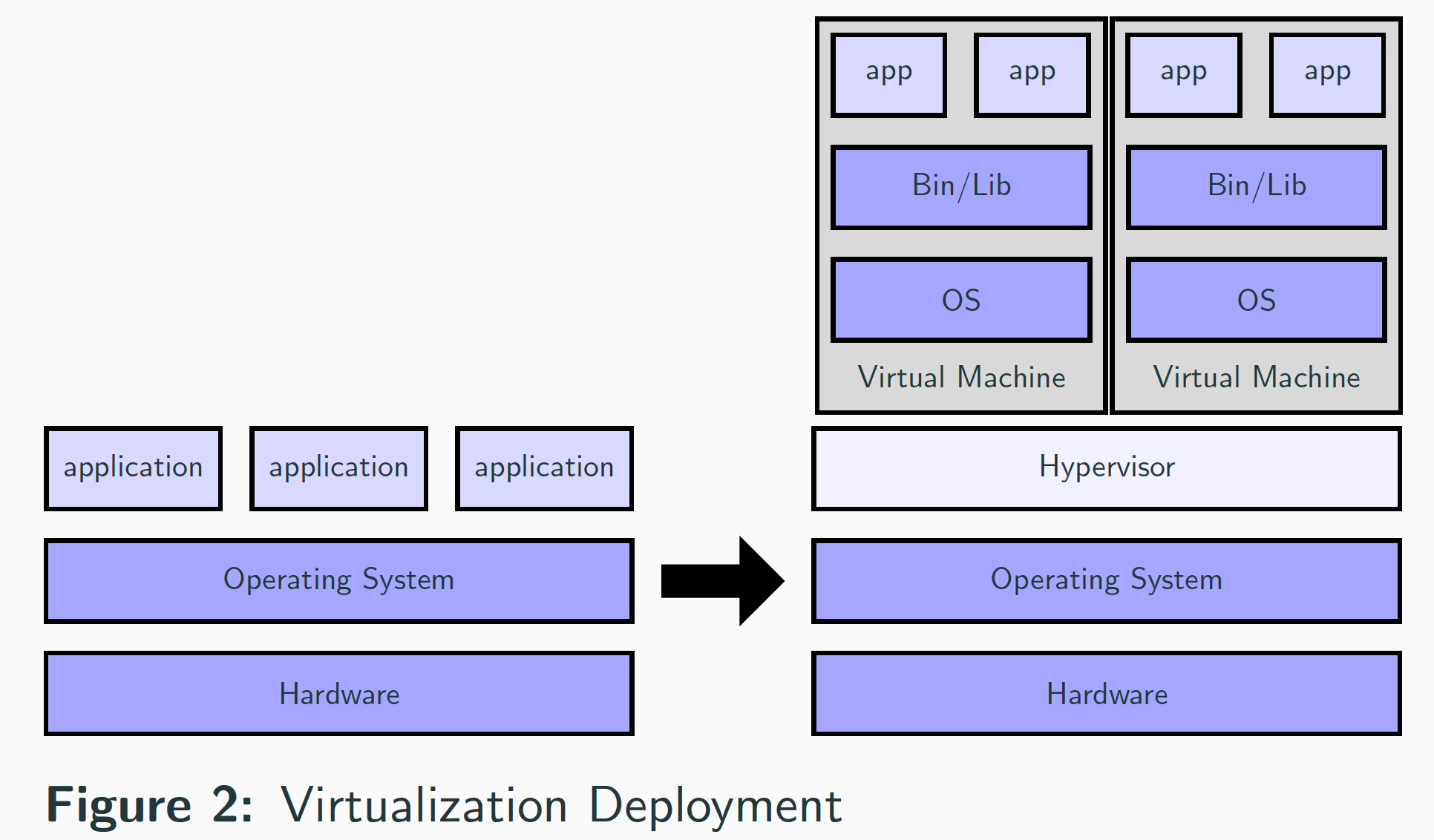
Hypervisor
- How is virtualization possible?
- A hypervisor is computer software, firmware or hardware that creates and runs virtual machines.
- The hypervisor allows multiple VMs to run on a single machine.
- The hypervisor has 2 types:
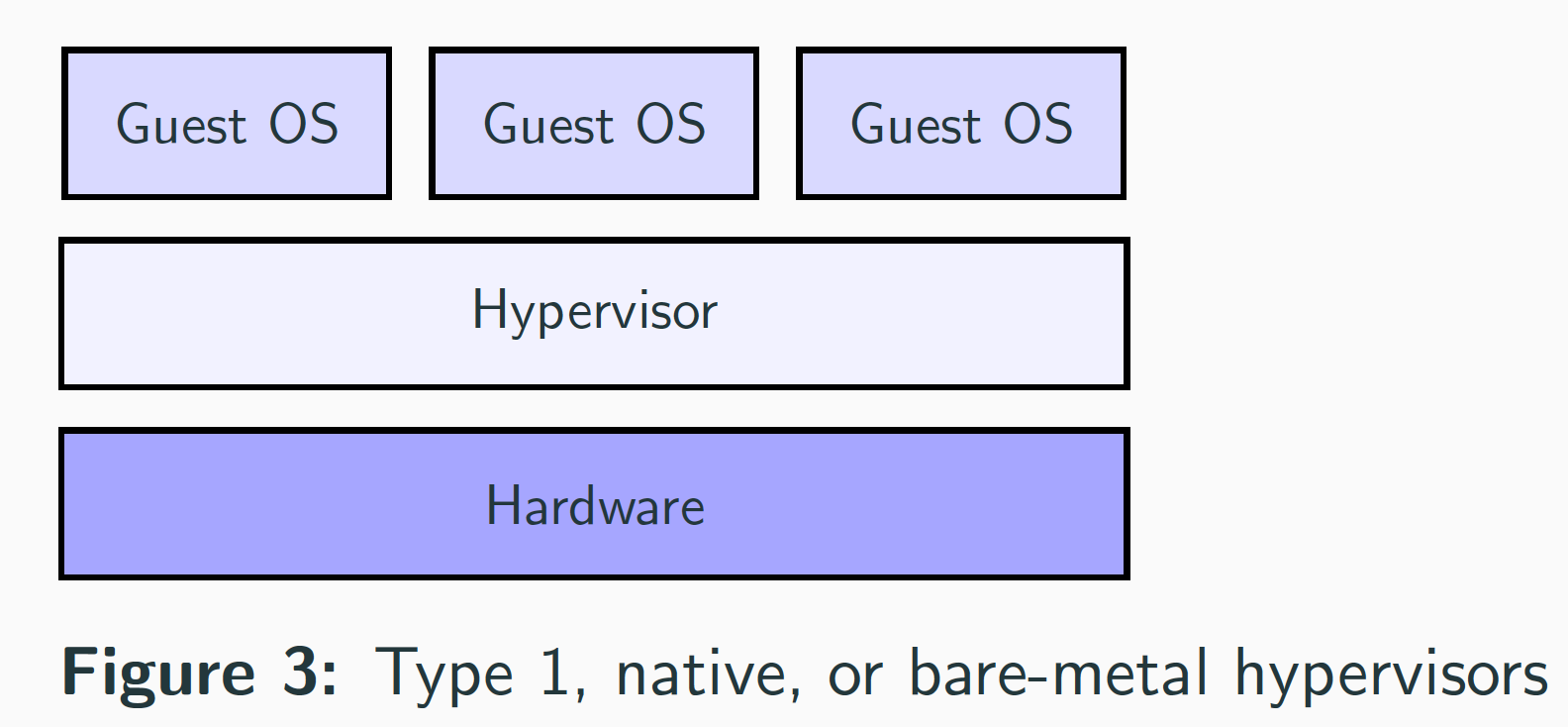
- Type 1 Hypervisor, native, or bare-metal hypervisors.
Example: VMware ESX and Citrix Xen servers.
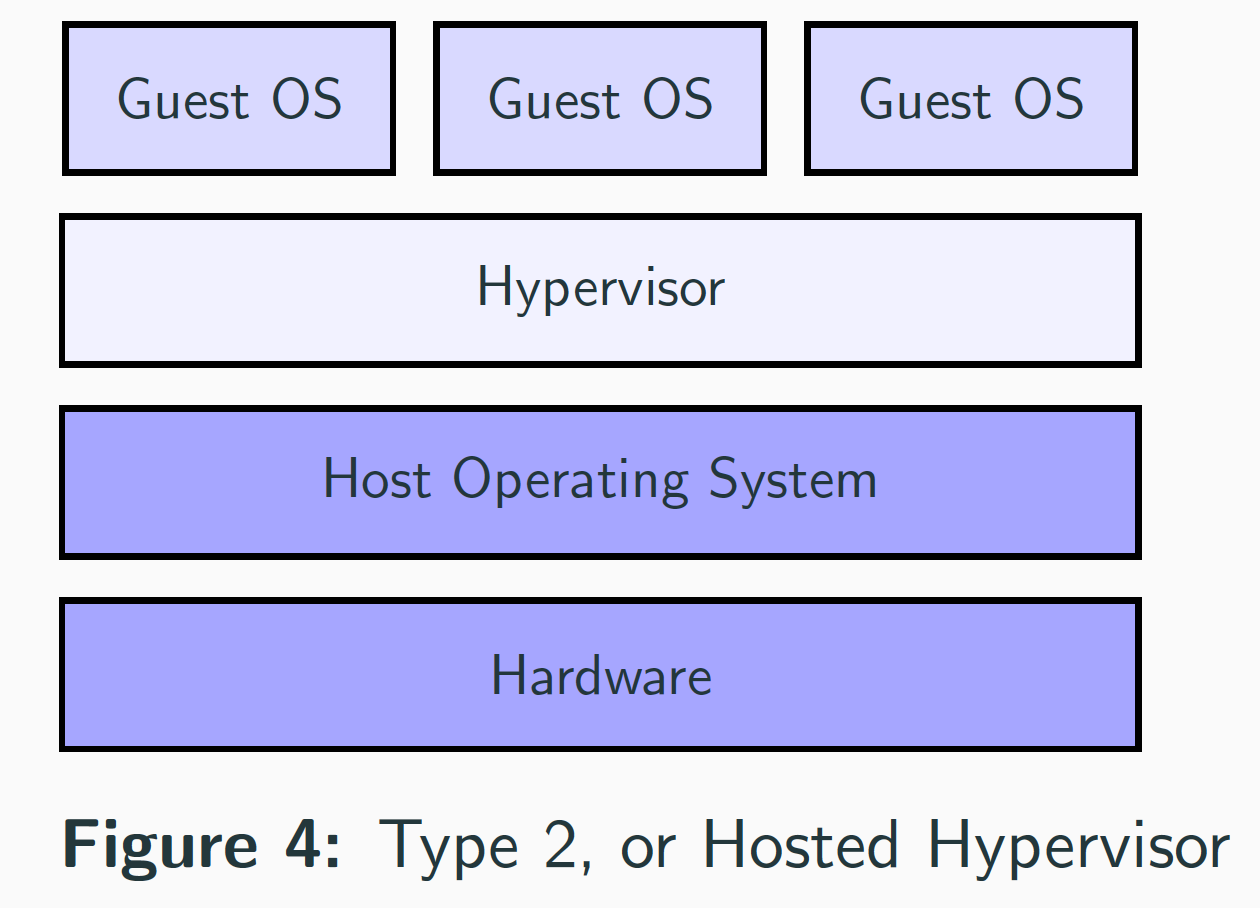
- Type 2 Hypervisor, or hosted hypervisors.
Type-2: VMware player and VirtualBox.
Containerization
Containers! What is a Container?
- The process of virtualizing the operating system produces containers.
- Container is a virtual operating system.
- A container is an abstraction at the OS layer that packages code and dependencies together as a standardized unit of software.
- Containers take up less space than VMs, boots quickly, and in isolation.
- Containerization eliminates infrastructure wasted resources and utilizes them.
Containerized Deployment
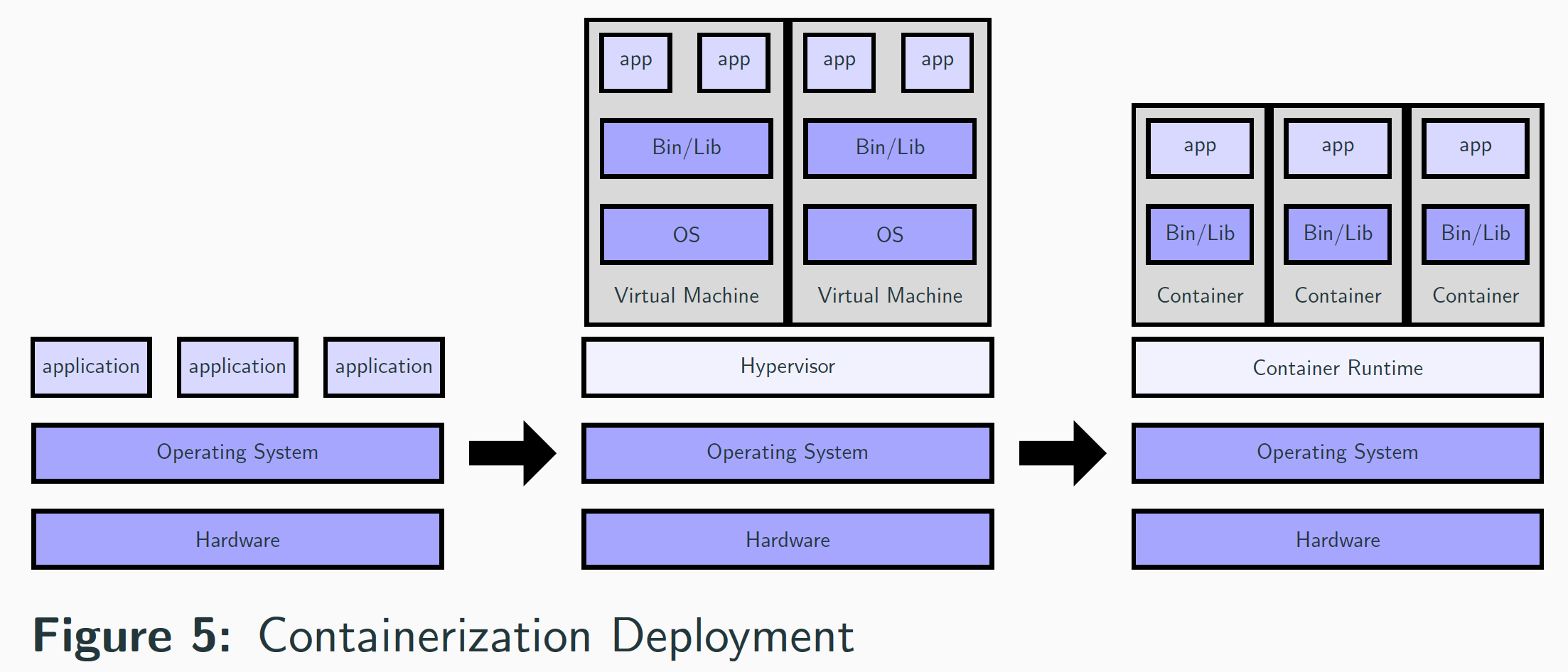
OS-level virtualization
How is containerization possible?
- OS-level virtualization refers to an operating system paradigm in which the operating system allows the existence of multiple isolated user-space instances (containers).
- OS-level virtualization solutions are the container engines.
- A container engine is a managed environment for deploying containerized applications.
User-space instances have different names
- Containers in \textbf{Docker} and Linux containers \textbf{LXC}.
- VPS in \textbf{OpenVZ}
- Virtual Kernel \textbf{DragonFly BSD}
Summary and Popular Questions
Summary
- The word virtualization applies to hardware and operating system.
- Hardware virtualization produces virtual machines.
- Operating system virtualization produces containers.
Why Containers are more popular?
- Containerization gives us better resource isolation with predictable application performance.
- Containerization gives us better resource utilization with high efficiency and density.
- They are loosely coupled, distributed, elastic, liberated micro-services.
- Environmental consistency across development, testing, and production
"It worked on my machine." - Agile application creation and deployment.
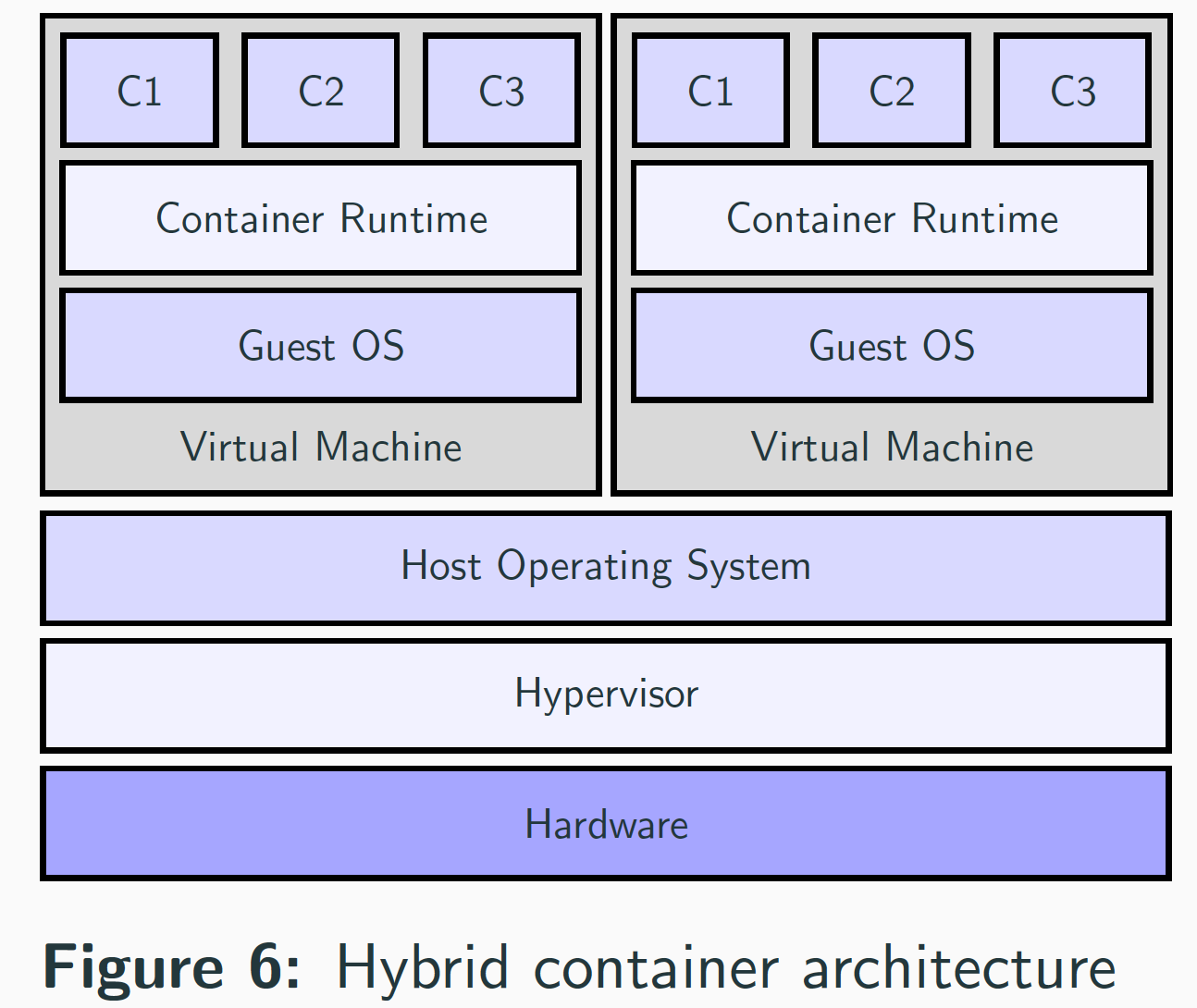
What is hybrid container architecture?
- hybrid container architecture is an architecture combining virtualization on both hardware and OS levels.
- Example: The container engine and associated containers execute on top of a virtual machine.
- Use of a hybrid container architecture is also known as hybrid containerization.
Do windows have native containers?
- You can have native windows containers but not Linux native containers yet.
- Microsoft’s native hypervisor solution is Hyper-V@.
- Using Hyper-V Microsoft supports running VMs natively on Windows, for example, Ubuntu on Windows (WSL).
- Microsoft is working on the OS-level virtualization solution to run Linux native containers.